Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
ORGAN-Specific Peptide Canine Safety Study
*Corresponding author:Jonathan RT Lakey, PhD, MSM, Professor Emeritus, University of California Irvine, CA, USA.
Received:May 19, 2022; Published: June 03, 2022
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2022.16.002236
Abstract
Extending the quality of life of companion pets is humane to pets and is of value to pet owners. Several veterinary life-saving therapeutic technologies have been proposed. We have developed novel peptide therapies for both clinical and companion pets using organ-specific stem cell derived peptides under the name Biopep Inc. Our first peptide therapy, EW-iJMP7, is comprised of signaling peptides that are associated with the maintenance of regular bone, cartilage, joint and synovial fluids and are found in the placenta, central nervous system, and thymus. In this study, we aim to determine the effect of Intramuscular (IM) de-livery of these well characterized peptides in canine models. We gave six adult dogs once weekly injection of the EW-iJMP7 cocktail intramuscularly. These animals were euthanized after 1 or 2 weeks. Blood analysis was conducted to assess whole blood count and chemistry prior to euthanasia. Liver, kidney, heart, and lung samples were collected after euthanasia for histopathology analysis. Our results indicated that EW-iJMP7 injection did not cause observable side effects in dogs’ appearance or behavior, however, it resulted in a Significant Reduction Of Platelet Count and ALT (SGPT) which remained within the normal range, and a significant increase of BUN/Creatinine ratio above the normal range. Data from this study will provide safety data on advancing this technology to assist and support further studies in animal models of longevity and arthritis in companion pets.
Keywords: Peptide, Stem cell treatment, Canine, In vivo safety, Study
Introduction
Peptides are linear polymers formed by a series of amino acid residues that are linked together by peptide bonds. Whereas proteins typically contain between 50 and 2000 amino acid residues and have a mean molecular weight between 5.5 and 22kDa, peptides are composed of less than 50 residues and accordingly, their weight range is below that of proteins. Short peptides have been demonstrated to play an important role in the modulation of transcription, transmission of biological information, and in restoring genetically conditioned alterations that occur with age [1,2]. These peptides are signaling molecules that act as regulatory factors through their interactions with DNA and histone proteins. Moreover, the physiological process of aging is highly influenced by the peptidergic regulation of homeostasis and is related to the aging of cells, tissues, and organs [3,4].
Peptide therapy aims to renew the strength of the signals received by cells to either induce peptide production or trigger normal signaling processes, thereby rejuvenating and revitalizing tissues, and the organism as a whole [5]. Although the contents of peptides are similar between cells, the function and morphology of the cell itself defines the content of bio-logically active substances and differences in ultrastructure [5]. Moreover, certain biologically active substances are predominantly synthesized or accumulated in specific tissues. Since the signaling activity and function of peptides is largely based on their cell type, peptide therapy can utilize organ-specific extracts to target diseased or aging tissue. Due to the short length of peptides and their low molecular weight, biosynthesis and extraction processes permit these peptides to be mass produced and distributed for use in therapeutic treatments. Through years of research and extensive global practice, MF+ Medical Labs has manufactured two products- Nano Organo Peptides (NOPs) and Mito Organelle (MO) Peptides-that are intended for use in both animals and humans as a revitalization therapy. The MOs are a mixture of organ-specific cellular extracts that are extracted from organ specific cells, homogenized, filtered, and sterilized [6]. They have a molecular weight of 500-700kDa and therefore must be given a healthcare worker via mesotherapy, intra-muscular or subcutaneous injection. They are believed to regenerate mitochondrial activity. These peptides have been administered to thousands of human patients over the past decade and no irritations have been noted.
Our first peptide therapy, EW-iMJP7, is an organ-specific Mito Organelle (MO) peptide preparation, comprised of seven organspecific peptides improves joint health and mobility. It is comprised of signaling peptides that are associated with the maintenance of regular bone, cartilage, joint and synovial fluids and found in the placenta, central nervous system, and thymus: MF+MO-Bone, MF+MO-Cartilage, MF+MO-Joint and Synovial Fluid, MF+MOPlacenta, MF+MO CNS, MF+MO Thymus. In this study, we aim to demonstrate safety of EW-iMJP7 injection into a limited number of dogs before advancing to a companion pet trial.
Materials and Methods
This study was performed under an independent IACUC reviewed and approved protocol (Calmi2 2022-127) at the CalMI2 facilities in San Diego, California. A total of six beagles, aged 6 months, were purchased from Marshall Farms. In this study, the dogs which were divided into two groups of three animals. The first group (n = 2 male, n = 1 female) was given a single injection of EWiMJP7 (1.4mg/kg) Intramuscular (IM) at the upper thigh on day 0, then was euthanized for tissue collection on Day 8. The second group (n =1 male, n = 2 female) was given injections on Day 0 and on Day 8. The latter group was then euthanized for tissue collection on Day 16 of the study.
Blood Analysis
Blood samples were drawn from the dogs’ jugular veins prior to
injections and prior to euthanasia. After injections were performed,
the dogs were observed during their daily exercise time to monitor
for im-mediate reactions or pain symptoms following injection. The
dogs’ health, appetite, and physical appearance were monitored
daily. Blood samples were analyzed for the following changes from
Day 0 to Days 7 and 14:
a. Complete blood count (TLC, MCV, MCH, MCHC, MPV and RDW,
PLT).
b. Blood chemistry including: GGT, AST, ALT, amylase, BUN,
glucose, albumin, cholesterol, uric acid, CK, creatinine TBL, TP,
globulin.
c. Behavioral observations.
Results
Behavioral observations, Complete Blood Count (CBC), and blood chemistry analysis results are shown below.
Behavioral changes
No behavioral changes were observed following the administration of EW-iMJP7 at Days 8 and 16 (Table 1).
Blood analysis
Blood analysis was performed on dogs 1, 2, and 3 at Day 0 and 7, and at Day 0 and 14 on dogs 4, 5, and 6. Complete Blood Count (CBC) and blood chemistry values are given in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively. White Blood Cell Count (WBC), Hemoglobin (HGB), total protein, albumin, Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, BUN/ creatinine ratio, cholesterol, and liver enzymes: Aspartate Transaminase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) were selected for further analysis. Differences in select mean values at Day 0, 7, and 14 were compared using paired two-tailed t-tests (α=0.05). Of the 11 values selected for further analysis, total protein and BUN at Day 14 had increased significantly from baseline values at Day 0 (p<0.05, n=3). Additionally, BUN/creatinine ratio was out of normal range on Day 7 and 14, and creatinine levels were out of normal range on Day 14. No other significant changes were observed, and all other values were within normal range. See Table 3 for a complete list of results.
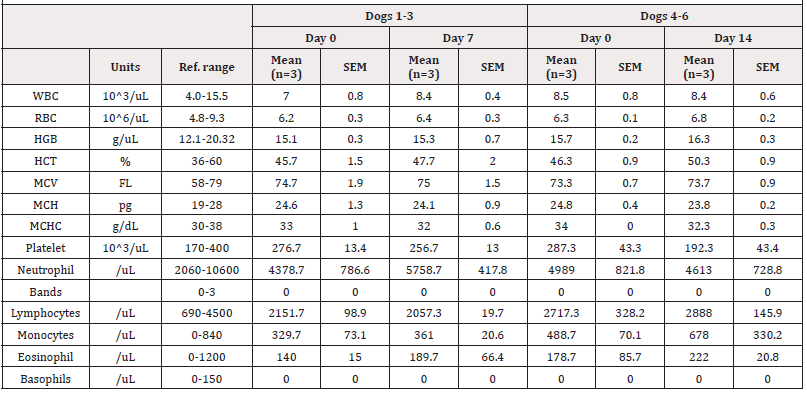
Table 2: Complete Blood Cell Count (CBC) before and after receiving EW-iMJP7 peptides at Days 0 and 7 (Dogs 1-3) and Day 0 and 14 (Dogs 4-6). The difference in select mean values (WBC, HGB) at Day 0 and 7 were determined in dogs 1-3, and Day 0 and 14 in dogs 4-6 and compared using a paired, two-tailed t-test (α=0.05, n=3). No significant differences in values were observed.
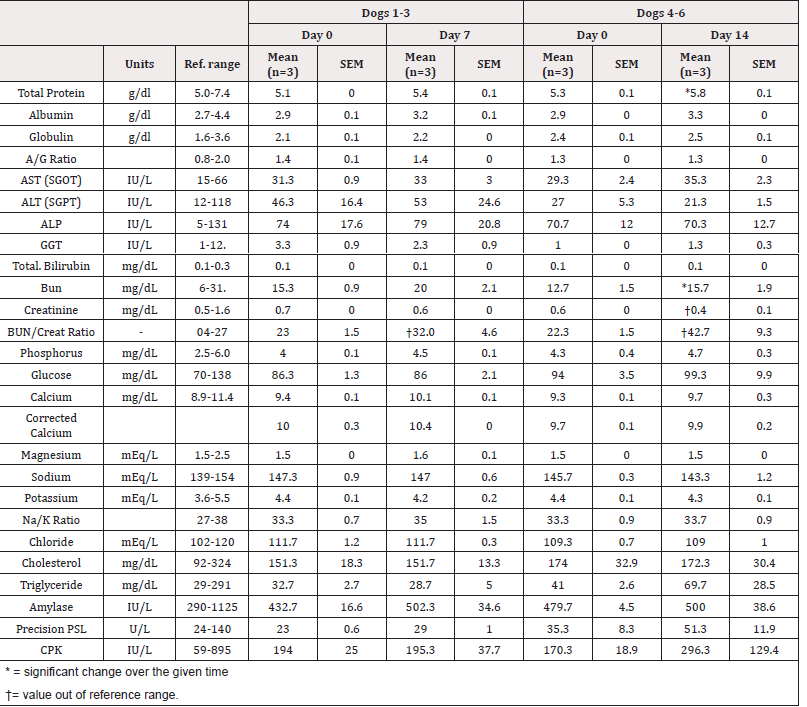
Table 3: Complete Blood Cell Count (CBC) before and after receiving EW-iMJP7 peptides at Days 0 and 7 (Dogs 1-3) and Day 0 and 14 (Dogs 4-6). The difference in select mean values (WBC, HGB) at Day 0 and 7 were determined in dogs 1-3, and Day 0 and 14 in dogs 4-6 and compared using a paired, two-tailed t-test (α=0.05, n=3). No significant differences in values were observed.
Discussion
The results from this study suggest that EW-iMJP7 peptide injection in dogs is well tolerated, with no safety concerns noted. No effects were observed in the dogs’ behavior; however, blood analysis showed some changes. This included a significant increase in total blood protein (+0.2g/dL) and Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) (+0.04mg/dL) at Day 14 (Table 4), however, these values remained within normal range. At Day 7, WBC, Hgb, albumin, cholesterol, and liver enzymes: AST, ALT, and ALP values were slightly elevated, and creatinine was slightly decreased compared to baseline at Day 0, although none of these changes were significant and all values remained within normal range (Table 4). At Day 14, HGB, albumin, and AST levels were elevated, and WBC, ALT, ALP, and cholesterol levels were lower compared to baseline values. None of these changes in blood chemistry were significant and each of the selected values remained within normal limits at both Day 7 and 14 (Table 4).
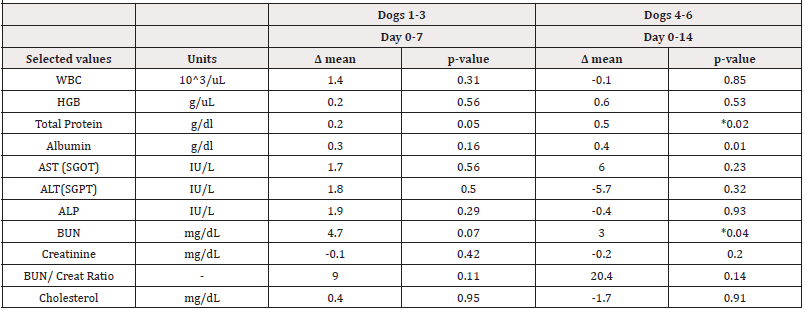
Table 4:Testing for significant changes to select Complete Blood Count (CBC) and blood chemistry values before and after receiving EW-iMJP7 peptides in dogs over a seven and fourteen-day period. Differences in mean values (Δ mean) were determined at Day 7 (dogs 1-3) and Day 14 (dogs 4-6) and compared using a paired, two-tailed t-test (α=0.05, n=3). An increase or decrease in value over the specified time is indicated by “ + ” or “ - “, respectively, and “ * “ represents a significant change in value.
Interestingly, the mean creatinine level was reduced below the nor-mal reference range at Day 14. In contrast, the BUN/ creatinine ratio was increased above the normal range at days 7 and 14 (Table 2) which indicates some impact on the reduction of blood flow to the kidneys. No de-hydration signs were observed within the fourteenday observation period. In future studies, a longer observation period is needed to determine whether the BUN level increase is an acute response, or a chronic response associated with other causes, such as stress, congestive heart failure, or gastrointestinal bleeding.
Conclusion
Data from this study provides important preliminary safety data that suggests that EW-iMJP7 peptides are well tolerated. Further, this data promises to advance this technology to assist and support additional animal models’ studies in longevity and arthritis in companion pets.




 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.